Using URDF with robot_state_publisher
Goal: Simulate a walking robot modeled in URDF and view it in Rviz.
Tutorial level: Intermediate
Time: 15 minutes
Contents
Background
This tutorial will show you how to model a walking robot, publish the state as a tf2 message and view the simulation in Rviz.
First, we create the URDF model describing the robot assembly.
Next we write a node which simulates the motion and publishes the JointState and transforms.
We then use robot_state_publisher to publish the entire robot state to /tf2.
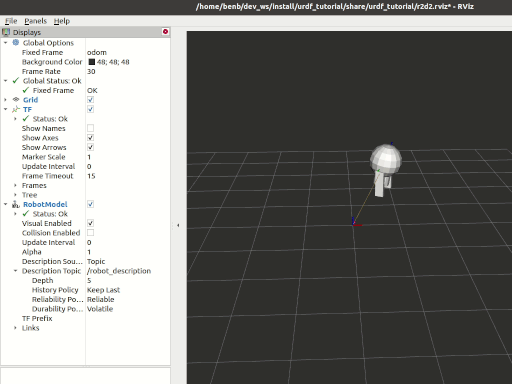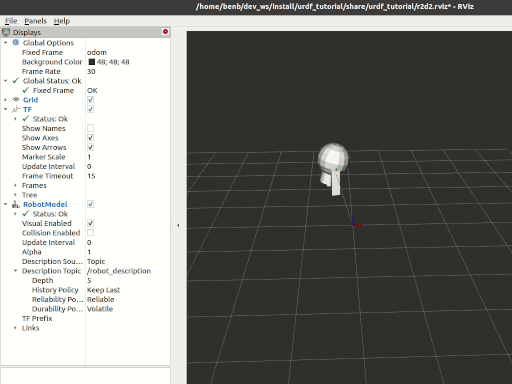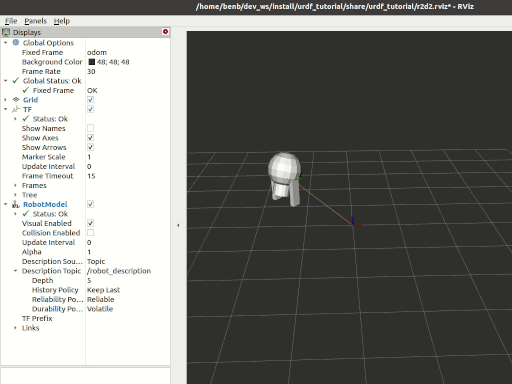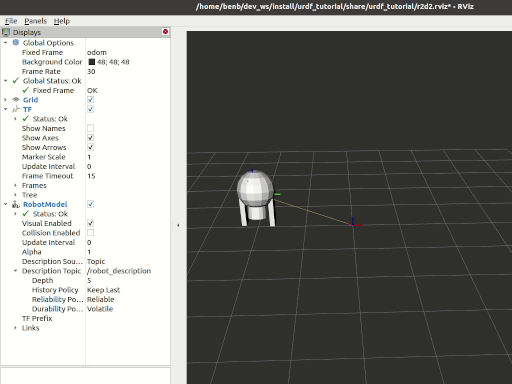
Tasks
1 Create a package
mkdir -p ~/dev_ws/src # change as needed
cd ~/dev_ws/src
ros2 pkg create urdf_tutorial_r2d2 --build-type ament_python --dependencies rclpy
cd urdf_tutorial_r2d2
You should now see a urdf_tutorial_r2d2 folder.
Next you will make several changes to it.
2 Create the URDF File
Create the directory where we will store some assets:
mkdir -p urdf
Download the URDF file and save it as ~/dev_ws/src/urdf_tutorial_r2d2/urdf/r2d2.urdf.xml.
Download the Rviz configuration file and save it as ~/dev_ws/src/urdf_tutorial_r2d2/urdf/r2d2.rviz.
3 Publish the state
Now we need a method for specifying what state the robot is in. To do this, we must specify all three joints and the overall odometry.
Fire up your favorite editor and paste the following code into ~/dev_ws/src/urdf_tutorial_r2d2/urdf_tutorial_r2d2/state_publisher.py
from math import sin, cos, pi
import rclpy
from rclpy.node import Node
from rclpy.qos import QoSProfile
from geometry_msgs.msg import Quaternion
from sensor_msgs.msg import JointState
from tf2_ros import TransformBroadcaster, TransformStamped
class StatePublisher(Node):
def __init__(self):
rclpy.init()
super().__init__('state_publisher')
qos_profile = QoSProfile(depth=10)
self.joint_pub = self.create_publisher(JointState, 'joint_states', qos_profile)
self.broadcaster = TransformBroadcaster(self, qos=qos_profile)
self.nodeName = self.get_name()
self.get_logger().info("{0} started".format(self.nodeName))
degree = pi / 180.0
loop_rate = self.create_rate(30)
# robot state
tilt = 0.
tinc = degree
swivel = 0.
angle = 0.
height = 0.
hinc = 0.005
# message declarations
odom_trans = TransformStamped()
odom_trans.header.frame_id = 'odom'
odom_trans.child_frame_id = 'axis'
joint_state = JointState()
try:
while rclpy.ok():
rclpy.spin_once(self)
# update joint_state
now = self.get_clock().now()
joint_state.header.stamp = now.to_msg()
joint_state.name = ['swivel', 'tilt', 'periscope']
joint_state.position = [swivel, tilt, height]
# update transform
# (moving in a circle with radius=2)
odom_trans.header.stamp = now.to_msg()
odom_trans.transform.translation.x = cos(angle)*2
odom_trans.transform.translation.y = sin(angle)*2
odom_trans.transform.translation.z = 0.7
odom_trans.transform.rotation = \
euler_to_quaternion(0, 0, angle + pi/2) # roll,pitch,yaw
# send the joint state and transform
self.joint_pub.publish(joint_state)
self.broadcaster.sendTransform(odom_trans)
# Create new robot state
tilt += tinc
if tilt < -0.5 or tilt > 0.0:
tinc *= -1
height += hinc
if height > 0.2 or height < 0.0:
hinc *= -1
swivel += degree
angle += degree/4
# This will adjust as needed per iteration
loop_rate.sleep()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
pass
def euler_to_quaternion(roll, pitch, yaw):
qx = sin(roll/2) * cos(pitch/2) * cos(yaw/2) - cos(roll/2) * sin(pitch/2) * sin(yaw/2)
qy = cos(roll/2) * sin(pitch/2) * cos(yaw/2) + sin(roll/2) * cos(pitch/2) * sin(yaw/2)
qz = cos(roll/2) * cos(pitch/2) * sin(yaw/2) - sin(roll/2) * sin(pitch/2) * cos(yaw/2)
qw = cos(roll/2) * cos(pitch/2) * cos(yaw/2) + sin(roll/2) * sin(pitch/2) * sin(yaw/2)
return Quaternion(x=qx, y=qy, z=qz, w=qw)
def main():
node = StatePublisher()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
4 Create a launch file
Create a new ~/dev_ws/src/urdf_tutorial_r2d2/launch folder.
Open your editor and paste the following code, saving it as ~/dev_ws/src/urdf_tutorial_r2d2/launch/demo.launch.py
import os
from ament_index_python.packages import get_package_share_directory
from launch import LaunchDescription
from launch.actions import DeclareLaunchArgument
from launch.substitutions import LaunchConfiguration
from launch_ros.actions import Node
def generate_launch_description():
use_sim_time = LaunchConfiguration('use_sim_time', default='false')
urdf_file_name = 'r2d2.urdf.xml'
urdf = os.path.join(
get_package_share_directory('urdf_tutorial_r2d2'),
urdf_file_name)
with open(urdf, 'r') as infp:
robot_desc = infp.read()
return LaunchDescription([
DeclareLaunchArgument(
'use_sim_time',
default_value='false',
description='Use simulation (Gazebo) clock if true'),
Node(
package='robot_state_publisher',
executable='robot_state_publisher',
name='robot_state_publisher',
output='screen',
parameters=[{'use_sim_time': use_sim_time, 'robot_description': robot_desc}],
arguments=[urdf]),
Node(
package='urdf_tutorial_r2d2',
executable='state_publisher',
name='state_publisher',
output='screen'),
])
5 Edit the setup.py file
You must tell the colcon build tool how to install your Python package.
Edit the ~/dev_ws/src/urdf_tutorial_r2d2/setup.py file as follows:
include these import statements
import os
from glob import glob
from setuptools import setup
from setuptools import find_packages
append these 2 lines inside
data_files
data_files=[
...
(os.path.join('share', package_name), glob('launch/*.py')),
(os.path.join('share', package_name), glob('urdf/*'))
],
modify the
entry_pointstable so you can later run ‘state_publisher’ from a console
'console_scripts': [
'state_publisher = urdf_tutorial_r2d2.state_publisher:main'
],
Save the setup.py file with your changes.
6 Install the package
cd ~/dev_ws
colcon build --symlink-install --packages-select urdf_tutorial_r2d2
source install/setup.bash
7 View the results
Launch the package
ros2 launch urdf_tutorial_r2d2 demo.launch.py
Open a new terminal, the run Rviz using
rviz2 -d ~/dev_ws/install/urdf_tutorial_r2d2/share/urdf_tutorial_r2d2/r2d2.rviz
See the User Guide for details on how to use Rviz.
Summary
You created a JointState publisher node and coupled it with robot_state_publisher to simulate a walking robot.
The code used in these examples can be found here.
Credit is given to the authors of this ROS 1 tutorial from which some content was reused.